根據controller的名字正確的實例化了一個controller對象回到MVCHandler的BeginProcessRequest方法可以看到當得到controller對象之後首先判斷它是不是IAsyncController如果是則會創建委托用來異步執行通常情況下我們都是繼承自Controller類這不是一個IAsyncController於是會直接執行Controller的Execute方法Execute方法是在Controller的基類ControllerBase中定義的這個方法除去一些安全檢查初始化了ControllerContext(包含了ControllerBase和Request的信息)核心是調用了ExecuteCore方法這在ControllerBase是個抽象方法在Controller類中有實現
復制代碼 代碼如下:
protected override void ExecuteCore() {
PossiblyLoadTempData();
try {
string actionName = RouteDataGetRequiredString(action);
if (!ActionInvokerInvokeAction(ControllerContext actionName)) {
HandleUnknownAction(actionName);
}
}
finally {
PossiblySaveTempData();
}}
這個方法比較簡單
首先是加載臨時數據
這僅在是child action的時候會出現
暫不討論
接下來就是獲取action的名字
然後InvokeAction
這裡的ActionInvoker是一個ControllerActionInvoker類型的對象
我們來看它的InvokeAction方法
復制代碼 代碼如下:
public virtual bool InvokeAction(ControllerContext controllerContext string actionName) {
if (controllerContext == null) {
throw new ArgumentNullException(controllerContext);
}
if (StringIsNullOrEmpty(actionName)) {
throw new ArgumentException(MvcResourcesCommon_NullOrEmpty actionName);
}
ControllerDescriptor controllerDescriptor = GetControllerDescriptor(controllerContext);
ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor = FindAction(controllerContext controllerDescriptor actionName);
if (actionDescriptor != null) {
FilterInfo filterInfo = GetFilters(controllerContext actionDescriptor);
try {
AuthorizationContext authContext = InvokeAuthorizationFilters(controllerContext filterInfoAuthorizationFilters actionDescriptor);
if (authContextResult != null) {
// the auth filter signaled that we should let it shortcircuit the request
InvokeActionResult(controllerContext authContextResult);
}
else {
if (controllerContextControllerValidateRequest) {
ValidateRequest(controllerContext);
}
IDictionary<string object> parameters = GetParameterValues(controllerContext actionDescriptor);
ActionExecutedContext postActionContext = InvokeActionMethodWithFilters(controllerContext filterInfoActionFilters actionDescriptor parameters);
InvokeActionResultWithFilters(controllerContext filterInfoResultFilters postActionContextResult);
}
}
catch (ThreadAbortException) {
// This type of exception occurs as a result of ResponseRedirect() but we specialcase so that
// the filters dont see this as an error
throw;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// something blew up so execute the exception filters
ExceptionContext exceptionContext = InvokeExceptionFilters(controllerContext filterInfoExceptionFilters ex);
if (!exceptionContextExceptionHandled) {
throw;
}
InvokeActionResult(controllerContext exceptionContextResult);
}
return true;
}
// notify controller that no method matched
return false;}
這是一個非常核心的方法
有很多工作在這裡面完成
ASP
NET MVC中有幾個以Descriptor結尾的類型
首先獲得ControllerDescriptor
這個比較簡單
實際返回的是ReflectedControllerDescriptor對象
第二步實際上是調用了ReflectedControllerDescriptor的FindAction方法
獲得ActionDescriptor
ActionDescriptor最重要的屬性是一個MethodInfo
這就是當前action name對應的Action的方法
FindAction方法內部實際上是調用了ActionMethodSelector的FindActionMethod來獲得MethodInfo
可以想象
這個方法將會反射controller的所有方法的名字
然後和action name匹配
實際上
ASP
NET還支持一些額外的功能
主要是
通過ActionNameAttribute屬性重命名action的名字
支持ActionMethodSelectorAttribute對action方法進行篩選
比如[HttpPost]之類的
下面簡單看下ActionMethodSelector的實現
大致分為
步
首先是在構造函數中調用了如下方法反射controller中的所有action方法:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
private void PopulateLookupTables() {
MethodInfo[] allMethods = ControllerTypeGetMethods(BindingFlagsInvokeMethod | BindingFlagsInstance | BindingFlagsPublic);
MethodInfo[] actionMethods = ArrayFindAll(allMethods IsValidActionMethod);
AliasedMethods = ArrayFindAll(actionMethods IsMethodDecoratedWithAliasingAttribute);
NonAliasedMethods = actionMethodsExcept(AliasedMethods)ToLookup(method => methodName StringComparerOrdinalIgnoreCase);
}FindActionMethod方法如下:
public MethodInfo FindActionMethod(ControllerContext controllerContext string actionName) {
List<MethodInfo> methodsMatchingName = GetMatchingAliasedMethods(controllerContext actionName);
methodsMatchingNameAddRange(NonAliasedMethods[actionName]);
List<MethodInfo> finalMethods = RunSelectionFilters(controllerContext methodsMatchingName);
switch (finalMethodsCount) {
case :
return null;
case :
return finalMethods[];
default:
throw CreateAmbiguousMatchException(finalMethods actionName);
} }
這個方法是很清晰的
找到重命名之後符合的
本身名字符合的
然後所有的方法判斷是否滿足ActionMethodSelectorAttribute的條件
最後或者返回匹配的MethodInfo
或者拋出異常
或者返回null
三個步驟的實現並不困難
不再分析下去
第三步是得到Filter
FilterInfo filterInfo = GetFilters(controllerContext
actionDescriptor);實際調用的是
FilterProviders
Providers
GetFilters(controllerContext
actionDescriptor);這裡的代碼風格和之前的不太一樣
特別喜歡用各種委托
讀代碼有點困難
估計不是同一個人寫的
下面的分析都直接給出實際執行的代碼
首先看下FilterProvider的構造函數:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
static FilterProviders() {
Providers = new FilterProviderCollection();
ProvidersAdd(GlobalFiltersFilters);
ProvidersAdd(new FilterAttributeFilterProvider());
ProvidersAdd(new ControllerInstanceFilterProvider());
}
回憶下ASP
NET給Action加上filter的方法一共有如下幾種
在Application_Start注冊全局filter
通過屬性給Action方法或者Controller加上filter
Controller類本身也實現了IActionFilter等幾個接口
通過重寫Controller類幾個相關方法加上filter
這三種方式就對應了三個FilterProvider
這三個Provider的實現都不是很困難
不分析了
到此為止
准備工作都好了
接下來就會執行Filter和Action
ASP
NET的Filter一共有
類
Filter Type
Interface
Description
Authorization
IAuthorizationFilter
Runs first
Action
IActionFilter
Runs before and after the action method
Result
IResultFilter
Runs before and after the result is executed
Exception
IExceptionFilter
Runs if another filter or action method throws an exception下面看其源代碼的實現
首先就是InvokeAuthorizationFilters:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
protected virtual AuthorizationContext InvokeAuthorizationFilters(ControllerContext controllerContext IList<IAuthorizationFilter> filters ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor) {
AuthorizationContext context = new AuthorizationContext(controllerContext actionDescriptor);
foreach (IAuthorizationFilter filter in filters) {
filterOnAuthorization(context);
if (contextResult != null) {
break;
}
}
return context;}
注意到在實現IAuthorizationFilter接口的時候
要表示驗證失敗
需要在OnAuthorization方法中將參數context的Result設置為ActionResult
表示驗證失敗後需要顯示的頁面
接下來如果驗證失敗就會執行context的Result
如果成功就要執行GetParameterValues獲得Action的參數
在這個方法內部會進行Model Binding
這也是ASP
NET的一個重要特性
另文介紹
再接下來會分別執行InvokeActionMethodWithFilters和InvokeActionResultWithFilters
這兩個方法的結構是類似的
只是一個是執行Action方法和IActionFilter
一個是執行ActionResult和IResultFilter
以InvokeActionMethodWithFilters為例分析下
復制代碼 代碼如下:
protected virtual ActionExecutedContext InvokeActionMethodWithFilters(ControllerContext controllerContext IList<IActionFilter> filters ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor IDictionary<string object> parameters) {
ActionExecutingContext preContext = new ActionExecutingContext(controllerContext actionDescriptor parameters);
Func<ActionExecutedContext> continuation = () =>
new ActionExecutedContext(controllerContext actionDescriptor false /* canceled */ null /* exception */) {
Result = InvokeActionMethod(controllerContext actionDescriptor parameters)
};
// need to reverse the filter list because the continuations are built up backward
Func<ActionExecutedContext> thunk = filtersReverse()Aggregate(continuation
(next filter) => () => InvokeActionMethodFilter(filter preContext next));
return thunk();
}
這段代碼有點函數式的風格
不熟悉這種風格的人看起來有點難以理解
用函數式編程語言的話來說
這裡的Aggregate其實就是foldr
foldr::(a
>b
>b)
>b
>[a]
>b
foldr 接受一個函數作為第一個參數
這個函數的參數有兩個
類型為a
b
返回類型為b
第二個參數是類型b
作為起始值
第三個參數是一個類型為a的數組
foldr的功能是依次將數組中的a 和上次調用第一個參數函數(f )的返回值作為f的兩個參數進行調用
第一次調用f的時候用起始值
對於C#來說
用面向對象的方式表示
是作為IEnummerable的一個擴展方法實現的
由於C# 不能直接將函數作為函數的參數傳入
所以傳入的是委托
說起來比較拗口
看一個例子
復制代碼 代碼如下:
static void AggTest()
{
int[] data = { };
var res = dataAggregate(String (str val) => str + valToString());
ConsoleWriteLine(res);
}
最後輸出的結果是String
回到InvokeActionMethodWithFilters的實現上來
這裡對應的類型a是IActionFilter
類型b是Func<ActionExecutedContext>
初始值是continuation
假設我們有
個filter
[f
f
f
]
我們來看下thunk最終是什麼
第一次
next=continue
filter=f
返回值 ()=>InvokeActionMethodFilter(f
preContext
continue)
第二次
next=()=>InvokeActionMethodFilter(f
preContext
continue)
filter=f
返回值
()=>InvokeActionMethodFilter(f
preContext
()=> InvokeActionMethodFilter(f
preContext
continue))
最終
thunk= ()=>InvokeActionMethodFilter(f
preContext
()=>InvokeActionMethodFilter(f
preContext
()=>InvokeActionMethodFilter(f
preContext
continue)));
直到 return thunk()之前
所有真正的代碼都沒有執行
關鍵是構建好了thunk這個委托
把thunk展開成上面的樣子
應該比較清楚真正的調用順序什麼樣的了
這裡花了比較多的筆墨介紹了如何通過Aggregate方法構造調用鏈
這裡有一篇文章專門介紹了這個
也可以參考下
想象下
如果filter的功能就是先遍歷調用f的Executing方法
然後調用Action方法
最後再依次調用f的Executed方法
那麼完全可以用迭代來實現
大可不必如此抽象復雜
關鍵是ASP
NET MVC對於filter中異常的處理還有一些特殊之處
看下InvokeActionMethodFilter的實現
復制代碼 代碼如下:
internal static ActionExecutedContext InvokeActionMethodFilter(IActionFilter filter ActionExecutingContext preContext Func<ActionExecutedContext> continuation) {
filterOnActionExecuting(preContext);
if (preContextResult != null) {
return new ActionExecutedContext(preContext preContextActionDescriptor true /* canceled */ null /* exception */) {
Result = preContextResult
};
}
bool wasError = false;
ActionExecutedContext postContext = null;
try {
postContext = continuation();
}
catch (ThreadAbortException) {
// This type of exception occurs as a result of ResponseRedirect() but we specialcase so that
// the filters dont see this as an error
postContext = new ActionExecutedContext(preContext preContextActionDescriptor false /* canceled */ null /* exception */);
filterOnActionExecuted(postContext);
throw;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
wasError = true;
postContext = new ActionExecutedContext(preContext preContextActionDescriptor false /* canceled */ ex);
filterOnActionExecuted(postContext);
if (!postContextExceptionHandled) {
throw;
}
}
if (!wasError) {
filterOnActionExecuted(postContext);
}
return postContext;
}
代碼有點長
首先就是觸發了filter的OnActionExecuting方法
這是方法的核心
接下來的重點是 postContext = continuation(); 最後是OnActionExecuted方法
結合上面的展開式
我們可以知道真正的調用順序將是:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
fExecuting>fExecuting>fExectuing>InvokeActionMethod>fExecuted>f>Executed>fExecuted
那麼
源代碼中的注釋 // need to reverse the filter list because the continuations are built up backward 的意思也很明了了
需要將filter倒序排一下之後才是正確的執行順序
還有一類filter是當異常發生的時候觸發的
在InvokeAction方法中可以看到觸發它的代碼放在一個catch塊中
IExceptionFilter的觸發流程比較簡單
不多做解釋了
唯一需要注意的是ExceptionHandled屬性設置為true的時候就不會拋出異常了
這個屬性在各種context下面都有
他們是的效果是一樣的
比如在OnActionExecuted方法中也可以將他設置為true
同樣不會拋出異常
這些都比較簡單
不再分析其源代碼
這篇文章比較詳細的介紹了filter流程中出現異常之後的執行順序
最後說下Action Method的執行
前面我們已經得到了methodInfo
和通過data binding獲得了參數
調用Action Method應該是萬事俱備了
mvc這邊的處理還是比較復雜的
ReflectedActionDescriptor會去調用ActionMethodDispatcher的Execute方法
這個方法如下:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
public object Execute(ControllerBase controller object[] parameters) {
return _executor(controller parameters);
}
此處的_executor是
delegate object ActionExecutor(ControllerBase controller
object[] parameters);_exectuor被賦值是通過一個方法
利用Expression拼出方法體
參數
代碼在(ActionMethodDispatcher
cs)
static ActionExecutor GetExecutor(MethodInfo methodInfo)此處就不貼出了
比較復雜
這裡讓我比較費解的是
既然MethodInfo和parameters都有了
直接用反射就可以了
為什麼還要如此復雜
我將上面的Execute方法改為:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
public object Execute(ControllerBase controller object[] parameters) {
return MethodInfoInvoke(controller parameters);
//return _executor(controller parameters);
}
運行結果是完全一樣的
我相信mvc源代碼如此實現一定有其考慮
這個需要繼續研究
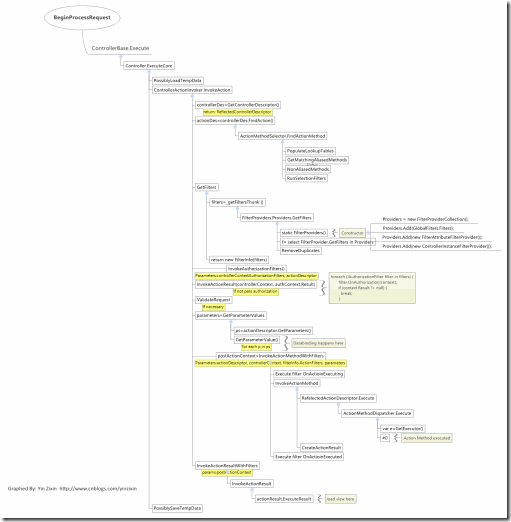
最後附上一張函數調用圖
以便理解
僅供參考
圖片較大
點擊可看原圖
From:http://tw.wingwit.com/Article/program/net/201404/30525.html

